2020 “Data-Empowered Evaluation Index of Government Administration” Released
Recently, Nankai University’s Research Center of Network Society Governance held a cloud conference and released the 2020 “Data-Empowered Evaluation Index of Government’s Governance Capability” together with the China Economic Information Service of Xinhua News Agency and the National Engineering Laboratory of Big Data Application Technology to Enhance Government’s Governance Capability. The result shows that Shanghai, Shenzhen and Beijing are among the top three, with Wuhan leaping to fourth, becoming the “black horse” of the year.
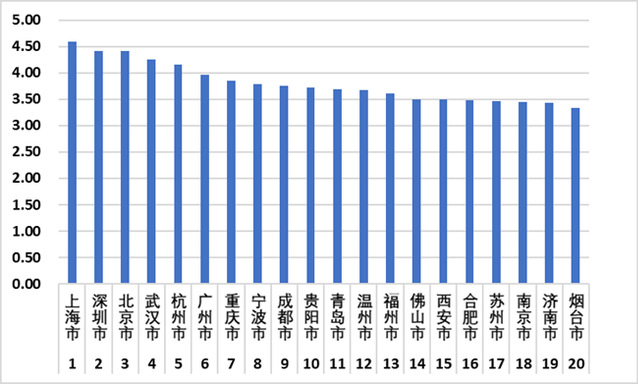
Developing from the “Evaluation Index of Big Data in Improving Government’s Governance Efficiency” released in 2019 Guiyang International Big Data EXPO, “Data-Empowered Evaluation Index of Government’s Governance Capability” has been upgraded and adjusted according to the latest development of digital government and raised the index weight of “digital infrastructure” and “new media of government affairs”. In addition to Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing and Wuhan, Hangzhou, Guangzhou, Chongqing, Ningbo, Chengdu and Guiyang ranked in the top ten of the 75 cities including municipalities directly under the central government, provincial capitals and prefecture level cities.
The report demonstrates that the overall performance of the eastern cities’ data-empowered governance is advantageous. The development power of the cities in the central region is considerable and Hefei has become the second major force in Central China after Wuhan. The cities in the western region show a trend of polarization: on the one hand, Chongqing, Chengdu and Guiyang are the leading cities; on the other hand, among the cities with lower scores, the western cities take up a large proportion. From the administrative level, the overall governance level of municipalities is the highest, and that of many provincial capitals is higher than the average level. Among prefecture level cities, except Shenzhen, Hangzhou and Ningbo, the overall scores of other cities are lower than those of the municipalities directly under the central government and provincial capital cities, and the scores decrease slowly with the ranking.
The evaluation index system of “Data-Empowered Evaluation Index of Government’s Governance Capability” includes four first-class indicators, which are governance effect, governance capacity, institutional guarantee and public participation. It consists of 18 second-class indicators such as administrative efficiency, digital economy and public service, and 24 third-class indicators. The results show that, consistent with last year, the overall performance of the system is still better than that of last year, and the capabilities of public participation and governance have been greatly improved compared with last year. Among the top 20 cities, Wuhan, Ningbo, Qingdao and Yantai are effect-supported cities; Guiyang and Fuzhou are institution-supported cities; Shanghai, Hangzhou and Guangzhou are effect-and-institution-supported cities; Shenzhen and Beijing are effect-and-public-participation-supported cities; Chongqing, Wenzhou, Hefei, Xi’an and Chengdu are institution-and-public-supported cities; Nanjing, Jinan, Foshan and Suzhou are balanced developing cities.
In addition to releasing online the “Data-Empowered Evaluation Index of Government’s Governance Capability”, Nankai University’s Research Center of Network Society Governance also cooperates with China Economic Information Service of Xinhua News Agency as a core force to carry on the research of “Data-Empowered Evaluation of Government’s Governance Capability and the Development of Anhui Province”. They compared the cities in the Yangtze River Delta region according to the evaluation index, and put forward countermeasures and suggestions for the development of Anhui Province. September 12, the result of the research was released in the “World Manufacturing Convention: Jianghuai Online Economic Forum” held in Anhui.

Scholars from Peking University, Tsinghua University, Fudan University, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Renmin University of China, Nanjing University, Huazhong University of science and technology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and Chongqing University congratulated on the successful release of the Index. They also made excellent reports on government data quality, digital supervision, government efficiency evaluation, government data openness, government data standards, blockchain and digital credit reporting system construction, government big data, and government new media. More than 400 people participated at the conference and the live broadcast online.
During the conference, people in charge of Nankai University’s Social Sciences Research Administration Office and Business School reviewed several influential “Nankai indexes” in the fields of economics and management. They also pointed out that the release of the Index by Nankai University’s Research Center of Network Society Governance is of great significance, reflecting the Nankai spirit of “knowing China and serving China”. They highly affirmed the research of Prof Fang Wang’s team in the field of big data and network social governance, and encouraged the Research Center to continue its efforts to make new achievements.
Prof Fang Wang said that the release of the index aims to summarize the latest achievements of the government in data empowered governance, and provide guidance and reference for future development. She hopes that the potential energy of “data tide” can endow the government with new vitality, make the government truly realize the dialogue, decision-making, service and innovation with data, and improve the governance efficiency and public service level through data empowerment.
( Reported by Qiandai Hu, Translated by Yuchen Shi, Edited by Davide Francolino and JianjingYun)