A Research Team from Nankai University Develops Nearest Paired Cloud for Robust and Fast Drift Correction for Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Pan Leiting and Prof. Xu Jingjun from the School of Physics and TEDA Institute of Applied Physics, Nankai University, in collaboration with Prof. Xu Ke’s research group at the University of California, Berkeley, USA, published a paper titled “Fast and robust drift correction for single-molecule localization microscopy” in Nature Communications. The study introduces the Nearest Paired Cloud (NPC) drift correction algorithm relying exclusively on coordinate information from localization data.
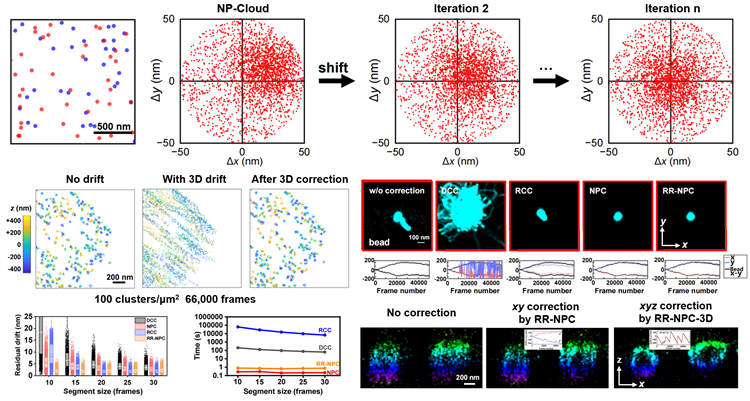
The research team divided tens of thousands of Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy (SMLM) images into multiple segments in chronological order, designating the first segment as the reference. The NPC algorithm first pairs the nearest-neighbor localization coordinates between two segments, then calculates a vectorial displacement between the paired positions. The resulting displacements for all localizations were pooled and plotted in two dimensions to generate an NPC diagram. The resulting diagram showed a high-density cloud, the center of which is shifted to the origin using an iterative mean-shift method. This resulting displacement vector is then applied to correct the drift between the corresponding segments. On this basis, the research team developed the Resampled-Reference NPC (RR-NPC) algorithm, which resamples a subset of frames from the NPC-corrected data to construct a new reference segment, and then performs an additional round of NPC-based drift correction. This algorithm further improves drift correction performance and pushes the resolution closer to the theoretical limit of SMLM. In terms of speed, NPC typically completes drift correction within seconds—>100-fold faster over the traditional Direct Cross-Correlation (DCC) method. RR-NPC achieves an even more dramatic improvement, operating >104 faster over Redundant Cross-Correlation (RCC) method, while also demonstrating higher robustness and precision.
In summary, the NPC and RR-NPC drift correction algorithms developed by the research team leverage the nanoscale precision of single-molecule localization data to deliver a robust, second-fast, nanometer-scale strategy for XYZ three-dimensional drift correction for SMLM. This approach significantly reduces SMLM’s reliance on specialized microscope hardware—particularly costly z-axis focus-locking systems—thereby lowering the overall cost of SMLM and promoting its broader, more accessible application.
The first author of this paper is Hou Mengdi, a Ph.D. candidate at NKU. Professors Pan Leiting and Xu Ke serve as the corresponding authors. Nankai University is listed as the primary affiliation.
Read the paper at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64085-8.
(Edited and translated by Nankai News Team.)