A Research Group at Nankai University Releases the 2024 China Insurance Institution Governance Index
On December 13, the China Insurance Institution Governance Evaluation Research Group at Nankai University released the 2024 China Insurance Institution Governance Index (CIIGI). Drawing on the latest annual disclosure data from China’s insurance sector, the 2024 CIIGI represents the index’s ninth annual release since its inaugural publication in 2016.
Led by Hao Chen, Associate Professor in the Department of Financial Management at Nankai Business School, the research group leveraged their long-term research expertise and drew on the mature methodology of the Chinese Corporate Governance Index (CCGINK) to design and establish China’s first insurance institution governance evaluation system based on publicly available information. The system was developed in adherence to the principles of scientific rigor, objectivity, systematic approach, feasibility, and dynamism, ensuring alignment with the specific conditions and unique governance characteristics of China’s insurance sector. CIIGI, also known as the Insurance Institution Governance Index of Nankai University (IIGINK), is compiled annually based on this system.
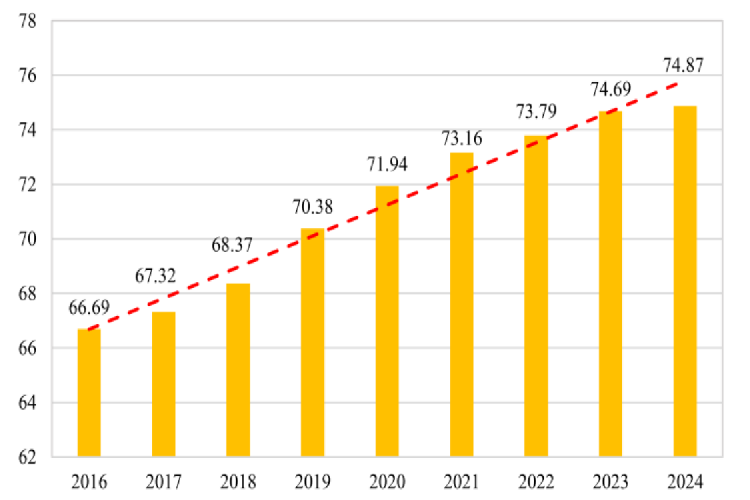
China Insurance Institution Governance Index 2016–2024
The evaluation for 2024 covered the entire population of 237 insurance institutions in China. The results showed that the 2024 CIIGI stood at 74.87, an increase of 0.18 from the 2023 score of 74.69, indicating steady improvement in the sector’s overall governance quality. From 2016 to 2024, the index maintained a general upward trajectory. The 2024 score represented a cumulative increase of 8.18 since the inception of the index in 2016. Notably, both the absolute annual increments and the year-on-year growth rates have moderated in recent years, indicating that the upward trend is stabilizing gradually.
NKU’s research group has proposed systematic recommendations for further enhancing the governance quality of Chinese insurance institutions. These recommendations are structured around three key stakeholders in China’s insurance sector: regulators, insurance institutions, and research institutions.

A Comparative Study on the Governance Quality of Chinese Insurance Institutions: Based on the CIIGI, which presents the research group’s latest findings based on the 2024 CIIGI, has recently been published by China Commerce and Trade Press. The book focuses on the governance landscape of Chinese insurance institutions in 2024 and adopts a comparative analysis to systematically elucidate the overall governance index, six content-specific sub-indices, two hierarchical sub-indices, and five categorical governance indices. This comprehensive, in-depth, and quantitative analysis reveals the current state of governance quality across China’s insurance sector.
CIIGI is hailed as a barometer of the governance quality of Chinese insurance institutions. To date, the research group has established a CIIGI database covering a nine-year period from 2016 to 2024, comprising a total of 566,300 data entries.
It is reported that Nankai University has maintained a profound tradition in index research since the release of its first Nankai Index in 1928. Statistics show that the Nankai Index family has grown to encompass over 400 members to date. Among them, governance-focused indices such as CCGINK, China Listed Company Green Governance Index (CGGINK), and the “Digital Intelligence Empowers Government Governance” evaluation index, represent significant contemporary extensions and advancements of this legacy. The continuous compilation and publication of CIIGI not only firmly upholds this Nankai Index legacy, but also constitutes a substantial expansion of the governance research framework.
(Edited and translated by Nankai News Team.)